LiDAR technology, an acronym for Light Detection and Ranging, has become an integral part of various industries, from autonomous vehicles to forestry management. This comprehensive guide delves into the workings of LiDAR, its applications, and its significance in today's technology-driven world..
Understanding LiDAR Technology
LiDAR operates on a simple yet sophisticated principle. It uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure distances. These light pulses—combined with other data recorded by the LiDAR system—generate precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics.
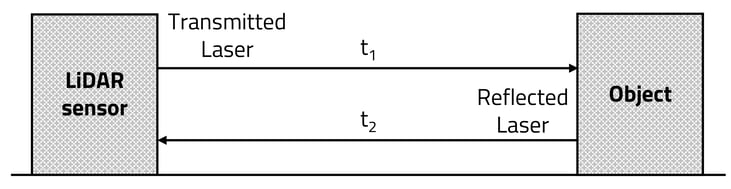
Source: Accuracy–Power Controllable LiDAR Sensor System with 3D Object Recognition for Autonomous Vehicle

Source: GeoSlam
The Core Components of a LiDAR System
A typical LiDAR system consists of four key components:
- Laser: At the heart of a LiDAR system is a laser. LiDAR lasers are capable of emitting light pulses at incredibly high rates. The wavelength of the laser light is a critical factor in determining the system's capabilities.
- Scanner and Optics: Steering the laser beams across the landscape, the scanner and its associated optics play a crucial role. The design and functionality of these components are pivotal in determining the LiDAR system's resolution and range.
- Photodetector and Receiver Electronics: After the laser light pulses hit an object and are reflected back, they are captured by the system's photodetector. The receiver electronics then process these signals. The time taken for the light to return is used to calculate distances.
- Positioning and Navigation Systems: Including a GPS receiver and an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU), these systems are crucial for accurate location and orientation data.
How LiDAR Maps the Physical World
Mapping using LiDAR technology involves emitting laser pulses toward the ground from an airborne system, such as a drone or an aircraft, or from a ground-based installation. As these pulses hit the ground and reflect back, the LiDAR sensor records the time taken for each pulse to return. Given the speed of light, this time can be translated into distance.
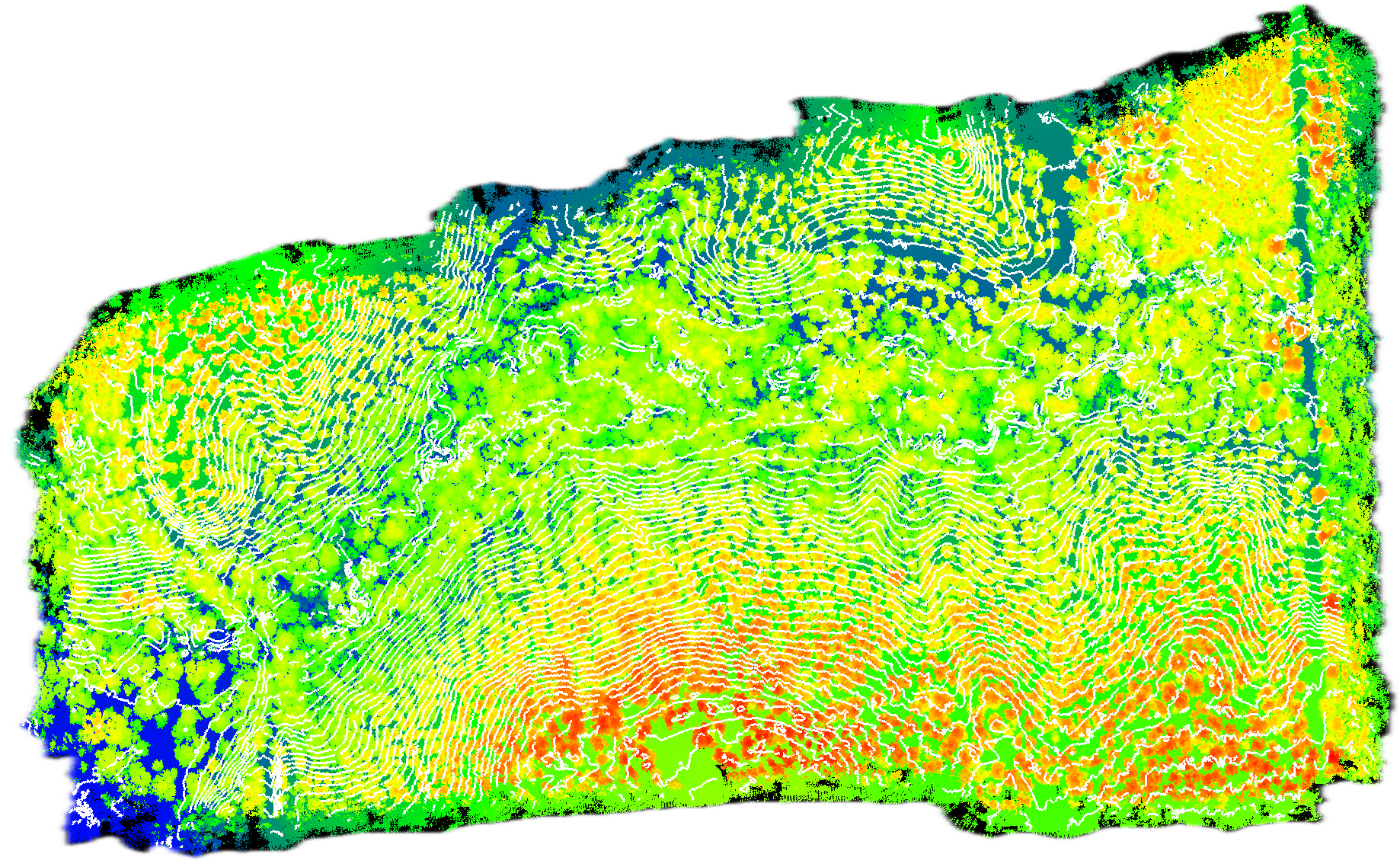
LiDAR Point Cloud Example
Combining these distances with the positioning data from the GPS and IMU, LiDAR systems create detailed 3D maps of the surveyed area. These maps are used in various applications, from creating topographical maps to helping autonomous vehicles navigate.
.gif?width=256&height=256&name=Lidar%20Basics%20-%20Final(HQ).gif) A colorized LiDAR point cloud overlaid on an orthomosaic.
A colorized LiDAR point cloud overlaid on an orthomosaic.
Applications of LiDAR Technology
LiDAR technology has found applications in numerous fields:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars use LiDAR to create a 3D map of their surroundings, enabling them to navigate safely. Explore how LiDAR is revolutionizing autonomous driving.
- Geology and Soil Science: LiDAR assists in studying natural landscapes, helping geologists understand erosion patterns, fault lines, and other geological features.
- Forestry and Agriculture: By analyzing canopy heights and densities, LiDAR helps in forest management and agricultural planning. Learn more about LiDAR in forestry management.
- Urban Planning: Urban planners use LiDAR to model cityscapes, aiding in the planning and development of urban infrastructure.
- Land Surveying: With the drone industry continually on the rise, land surveyors are looking to UAVs equipped with LiDAR for it’s ability to penetrate through dense vegetation and trees and reveal the ground below. This greatly improves surveyors' efficiency and speed.
- Historical and Archaeological Research: LiDAR has proven instrumental in uncovering ancient settlements and understanding historical landscapes.
- Flood Modeling and Coastal Management: LiDAR helps in creating accurate flood models and understanding coastal erosion, which is crucial for disaster management and mitigation efforts.
SUCCESS STORY: How Our Drone Mapping Services Helped A Surveyor Overcome Challenges
The Future of LiDAR
As technology advances, LiDAR systems are becoming more compact, affordable, and accessible. This democratization of LiDAR technology is opening up new possibilities and applications. We are likely to see LiDAR being integrated into smartphones, used for more advanced virtual reality experiences, and playing a significant role in environmental monitoring and conservation efforts.
LiDAR technology, with its ability to capture high-resolution, three-dimensional data, has become a cornerstone in surveying, mapping, and numerous other applications. As we continue to explore and understand our world, the importance of LiDAR technology cannot be overstated. With each passing day, LiDAR is not just mapping our world—it's shaping our future.
Looking for professional drone mapping services? Reach out to us for a comprehensive range of drone services, including high-quality orthomosaics and 1-foot contours.
Get an instant estimate today with our professional services Job Calculator.